5.5.1 Purpose
The purpose of Approve Requirements is to obtain agreement on and approval of requirements and designs for business analysis work to continue and/or solution construction to proceed.
5.5.2 Description
Business analysts are responsible for ensuring clear communication of requirements, designs, and other business analysis information to the key stakeholders responsible for approving that information.
Approval of requirements and designs may be formal or informal. Predictive approaches typically perform approvals at the end of the phase or during planned change control meetings. Adaptive approaches typically approve requirements only when construction and implementation of a solution meeting the requirement can begin. Business analysts work with key stakeholders to gain consensus on new and changed requirements, communicate the outcome of discussions, and track and manage the approval.
5.5.3 Inputs
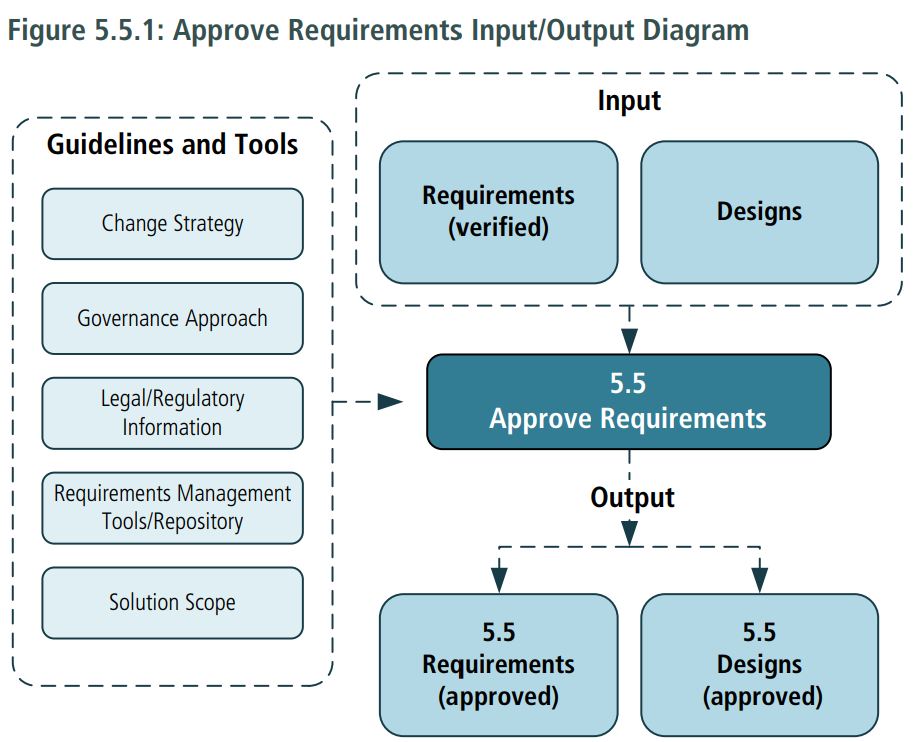
- Requirements (verified): a set of requirements that have been verified to be of sufficient quality to be used as a reliable body of work for further specification and development.
- Designs: a set of designs that have been determined as ready to be used for further specification and development.
5.5.4 Elements
.1 Understand Stakeholder Roles
The approval process is defined by the task Plan Business Analysis Governance (p. 37). Part of defining the approval process is understanding stakeholder roles and authority levels. Business analysts are responsible for obtaining stakeholder approvals and are required to understand who holds decision-making responsibility and who possesses authority for sign-off across the initiative.
Business analysts also consider any influential stakeholders who should be consulted or informed about the requirements. Few stakeholders may have the authority to approve or deny changes, but many stakeholders may be able to influence these decisions.
.2 Conflict and Issue Management
To maintain stakeholder support for the solution, consensus among stakeholders is usually sought prior to requesting approval of requirements. The approach for determining how to secure decisions and resolve conflicts across an initiative is planned for in the task Plan Business Analysis Governance (p. 37).
Stakeholder groups frequently have varying points of view and conflicting priorities. A conflict may arise among stakeholders as a result of different interpretations of requirements or designs and conflicting values placed on them.
The business analyst facilitates communication between stakeholders in areas of conflict so that each group has an improved appreciation for the needs of the others. Conflict resolution and issue management may occur quite often, as the business analyst is reviewing requirements and designs, and aiming to secure sign-off.
.3 Gain Consensus
Business analysts are responsible for ensuring that the stakeholders with approval authority understand and accept the requirements. Approval may confirm that stakeholders believe that sufficient value will be created for the organization to justify investment in a solution. Business analysts obtain approval by reviewing the requirements or changes to requirements with the accountable individuals or groups and requesting that they approve, indicating their agreement with the solution or designs described.
Using the methods and means established in the tasks Plan Business Analysis Governance (p. 37) and Communicate Business Analysis Information (p. 67) business analysts present the requirements to stakeholders for approval. Business analysts facilitate this approval process by addressing any questions or providing additional information when requested.
Complete agreement may not be necessary for a successful change, but if there is a lack of agreement, the associated risks are to be identified and managed accordingly.
.4 Track and Communicate Approval
The business analyst records approval decisions, possibly in requirements maintenance and tracking tools. In order to communicate the status of requirements, it is necessary to keep accurate records of current approval status.
Stakeholders must be able to determine what requirements and designs are currently approved and in line for implementation. There may be value in maintaining an audit history of changes to requirements: what was changed, who made the change, the reason for the change, and when it was made.
5.5.5 Guidelines and Tools
- Change Strategy: provides information which assists in managing stakeholder consensus regarding the needs of all stakeholders.
- Governance Approach: identifies the stakeholders who have the authority and responsibility to approve business analysis information and explains when such approvals will take place and how they will align to organizational policies.
- Legal/Regulatory Information: describes legislative rules or regulations that must be followed. They may impact the requirements and designs approval process.
- Requirement Management Tools/Repository: tool to record requirements approvals.
- Solution Scope: must be considered when approving requirements to accurately assess alignment and completeness.
5.5.6 Techniques
- Acceptance and Evaluation Criteria: used to define approval criteria.
- Decision Analysis: used to resolve issues and gain agreement.
- Item Tracking: used to track issues identified during the agreement process.
- Reviews: used to evaluate requirements.
- Workshops: used to facilitate obtaining approval.
5.5.7 Stakeholders
- Customer: may play an active role in reviewing and approving requirements and designs to ensure needs are met.
- Domain Subject Matter Expert: may be involved in the review and approval of requirements and designs as defined by stakeholder roles and responsibilities designation.
- End User: people who use the solution, or who are a solution component, and may be involved in the review, validation, and prioritization of requirements and designs as defined by the stakeholder roles and responsibilities designation.
- Operational Support: responsible for ensuring that requirements and designs are supportable within the constraints imposed by technology standards and organizational capability plans. Operational support personnel may have a role in reviewing and approving requirements.
- Project Manager: responsible for identifying and managing risks associated with solution design, development, delivery, implementation, operation and sustainment. The project manager may manage the project plan activities pertaining to review and/or approval.
- Regulator: external or internal party who is responsible for providing opinions on the relationship between stated requirements and specific regulations, either formally in an audit, or informally as inputs to requirements life cycle management tasks.
- Sponsor: responsible to review and approve the business case, solution or product scope, and all requirements and designs.
- Tester: responsible for ensuring quality assurance standards are feasible within the business analysis information. For example, requirements have the testable characteristic.
5.5.8 Outputs
- Requirements (approved): requirements which are agreed to by stakeholders and are ready for use in subsequent business analysis efforts.
- Designs (approved): designs which are agreed to by stakeholders and are ready for use in subsequent business analysis or solution development efforts.