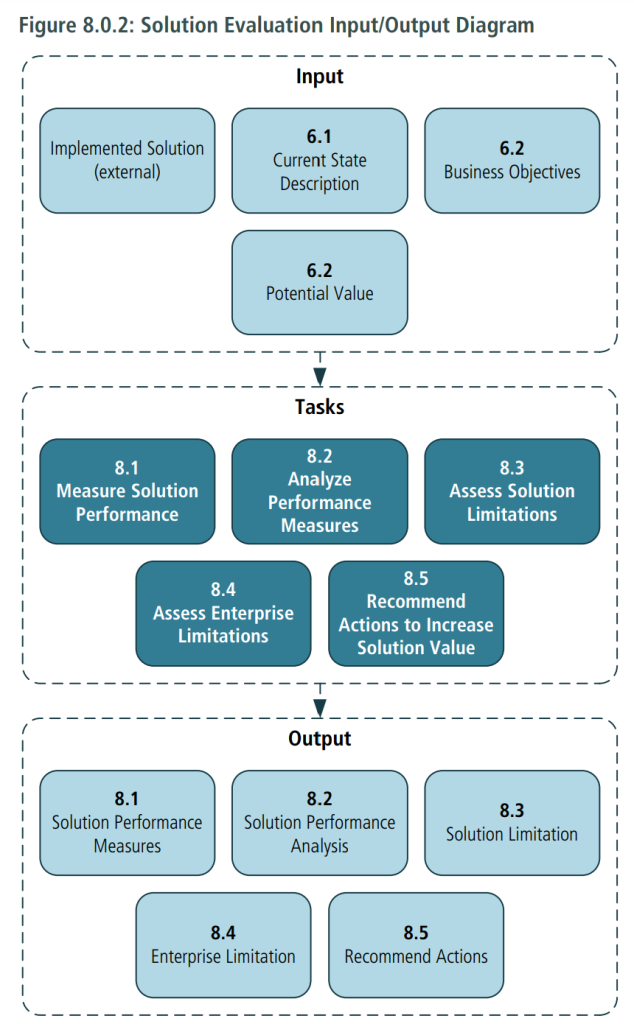
The Solution Evaluation knowledge area describes the tasks that business analysts perform to assess the performance of and value delivered by a solution in use by the enterprise, and to recommend removal of barriers or constraints that prevent the full realization of the value.
While there may be some similarities to the activities performed in Strategy Analysis (p. 99), or Requirements Analysis and Design Definition (p. 133), an important distinction between the Solution Evaluation knowledge area and other knowledge areas is the existence of an actual solution. It may only be a partial solution, but the solution or solution component has already been implemented and is operating in some form. Solution Evaluation tasks that support the realization of benefits may occur before a change is initiated, while current value is assessed, or after a solution has been implemented.
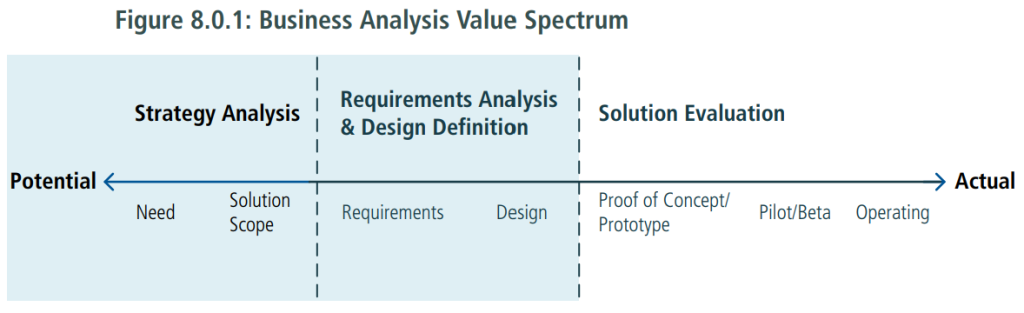
Solution Evaluation tasks can be performed on solution components in varying stages of development:
- Prototypes or Proofs of Concept: working but limited versions of a solution that demonstrate value.
- Pilot or Beta releases: limited implementations or versions of a solution used in order to work through problems and understand how well it actually delivers value before fully releasing the solution.
- Operational releases: full versions of a partial or completed solution used to achieve business objectives, execute a process, or fulfill a desired outcome.
Solution Evaluation describes tasks that analyze the actual value being delivered, identifies limitations which may be preventing value from being realized, and makes recommendations to increase the value of the solution. It may include any combination of performance assessments, tests, and experiments, and may combine both objective and subjective assessments of value. Solution Evaluation generally focuses on a component of an enterprise rather than the entire enterprise.
The following image illustrates the spectrum of value as business analysis activities progress from delivering potential value to actual value.
The Solution Evaluation knowledge area includes the following tasks:
- Measure Solution Performance: determines the most appropriate way to assess the performance of a solution, including how it aligns with enterprise goals and objectives, and performs the assessment.
- Analyze Performance Measures: examines information regarding the performance of a solution in order to understand the value it delivers to the enterprise and to stakeholders, and determines whether it is meeting current business needs.
- Assess Solution Limitations: investigates issues within the scope of a solution that may prevent it from meeting current business needs.
- Assess Enterprise Limitations: investigates issues outside the scope of a solution that may be preventing the enterprise from realizing the full value that a solution is capable of providing.
- Recommend Actions to Increase Solution Value: identifies and defines actions the enterprise can take to increase the value that can be delivered by a solution.
The Core Concept Model in Solution Evaluation
The Business Analysis Core Concept Model™ (BACCM™) describes the relationships among the six core concepts. The following table describes the usage and application of each of the core concepts within the context of Solution Evaluation.
| Core Concept | During Solution Evaluation, business analysts… |
|---|---|
| Change: the act of transformation in response to a need. | recommend a change to either a solution or the enterprise in order to realize the potential value of a solution |
| Need: a problem or opportunity to be addressed. | evaluate how a solution or solution component is fulfilling the need. |
| Solution: a specific way of satisfying one or more needs in a context. | assess the performance of the solution, examine if it is delivering the potential value, and analyze why value may not be realized by the solution or solution component. |
| Stakeholder: a group or individual with a relationship to the change, the need, or the solution. | elicit information from the stakeholders about solution performance and value delivery. |
| Value: the worth, importance, or usefulness of something to a stakeholder within a context. | determine if the solution is delivering the potential value and examine why value may not be being realized. |
| Context: the circumstances that influence, are influenced by, and provide understanding of the change. | consider the context in determining solution performance measures and any limitations within the context that may prohibit value from being realized. |
Table 8.0.1: The Core Concept Model in Solution Evaluation